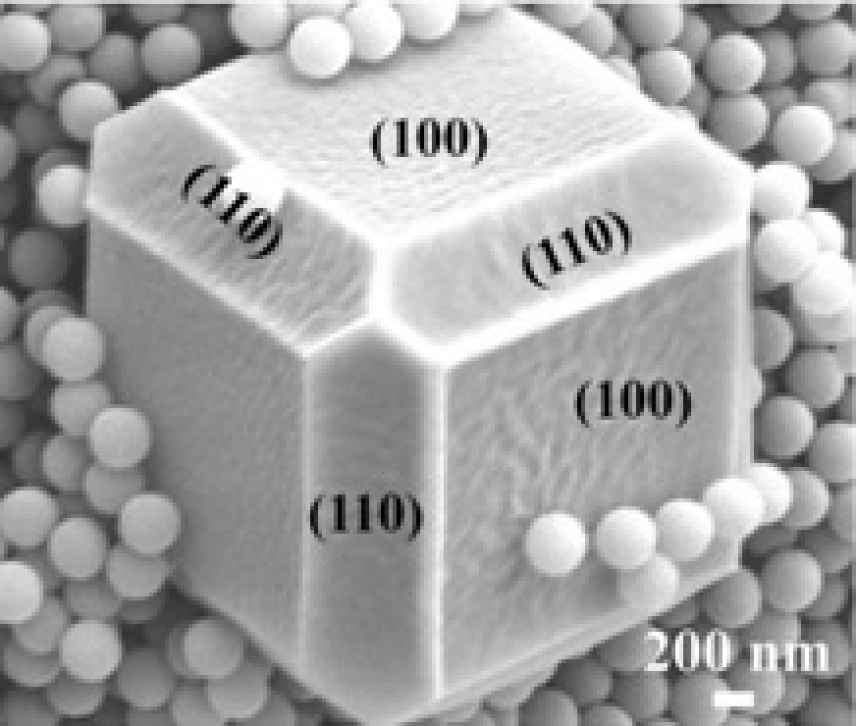
Porous materials make it possible to have nanotechnology under control
Escrito por UCC+iA University of Cordoba research team is able to stabilize different metallic nanostructures by encapsulating them in porous monocrystalline materials
Half metal, half organic structure, like Robocop himself, is the material known as MOF, short for Metal Organic Framework. MOF has been developed by scientists and applied to a myriad of products from sorbents to batteries for electronic devices. This material emerged from the nanotechnology revolution that turned material design upside down and facilitated the improvement of chemical processes. MOFs are a new organic and inorganic hybrid material made up of metallic nodes and organic links characterized by their porosity, that is to say, by the intermolecular spaces that it is comprised of.
Artificial intelligence combats the noise from diesel engines
Escrito por UCC+iSeveral University of Cordoba research teams have created a new system to predict the sound from these engines depending on the chemical physical composition of the biofuel
For years now, diesel engines have been one of the greatest competitors in the car industry. In spite of their advantages such as durability and affordability, one of their weaknesses continues to be the noise they produce. Now, a new model, designed by several University of Cordoba research groups, allows for predicting this noise depending on the chemical physical composition of the biofuel that powers the engine.
A tool based on the use ofcarbon nanoparticles enables detection of antidepressants in urine samples
Escrito por UCC+iThe test can be used to monitor therapeutic dosages, for cases of intoxication due to overdose or at a forensic level
A University of Cordoba research group has designed a tool that enables detection of antidepressants in urine samples in low concentrations. This new method is based on the developmentof a new material, based on carbon nanotubes, on the inside of pipette tips, the kinds that are normally used in analysis laboratories.
Researchers analyse the effect of C02pressure on the aroma of sparkling wines
Escrito por UCC+iAn UCO research team is studying the effect of carbon dioxide pressure on yeast metabolism during the second fermentation of sparkling wines
During alcoholic fermentation, yeasts turn sugar into ethanol and CO2gas. The gas forms the small bubbles which distinguish sparkling wines from “still” wines. High-quality sparkling wines are made using the traditional method, which requires a second alcoholic fermentation of a base wine – to which sugar and yeasts are added – in sealed bottles, followed by an interval of ageing in contact with yeast lees. This method was first described by the Benedictine monk Dom Pierre Pèrignon (1638-1715). When sugar is added to a wine and a second fermentation is carried out in an open container, the C02 produced is released into the atmosphere; however, when the second fermentation is carried out in a sealed container or bottle, the CO2overpressure released affects yeast metabolism.
A new method is being developed to assess the odorous impact of composting
According to some estimates, every year over 8,000 million tonnes of urban waste are generated worldwide, and there is every reason to believe that this figure will increase over the coming years due to population growth. One process that seeks to find a use for part of this huge amount of waste is composting, by which organic waste is converted into fertiliser.
Improved perovskite stability for third-generation solar cells
Escrito por UCC+iResearch at the University of Córdoba, published in Nature Energy, has led to the stabilisation of perovskite solar cells using guanidinium.
Increasing concern regarding the exhaustion of traditional energy sources has triggered a race to find alternatives. The development of solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity, is constantly advancing.